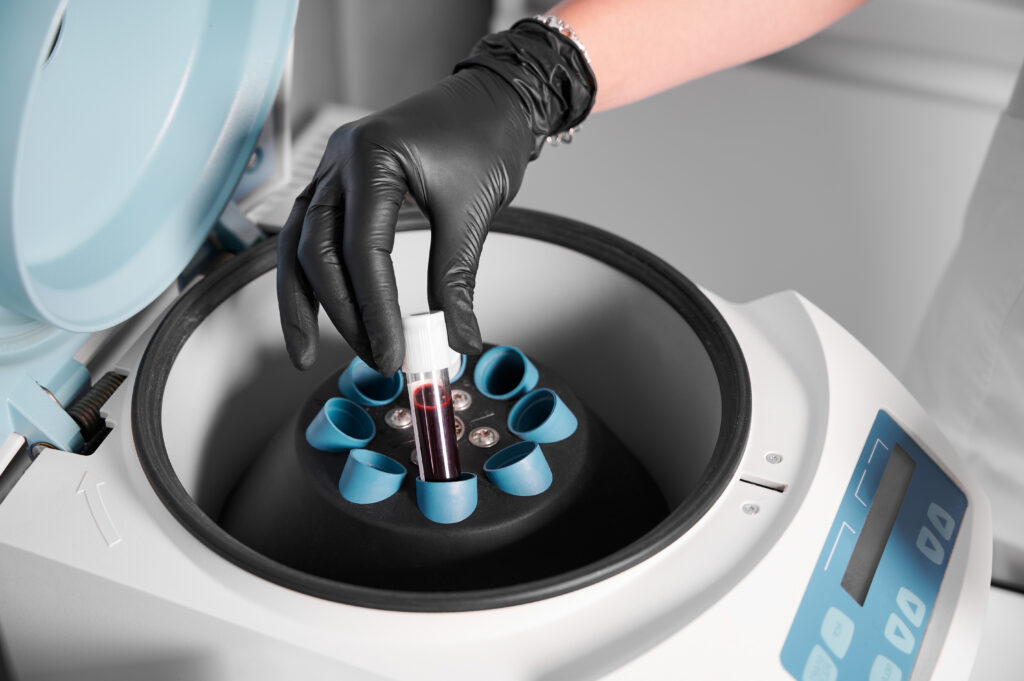
What is a Centrifuge? Functions, Uses, and Maintenance in Medical Labs
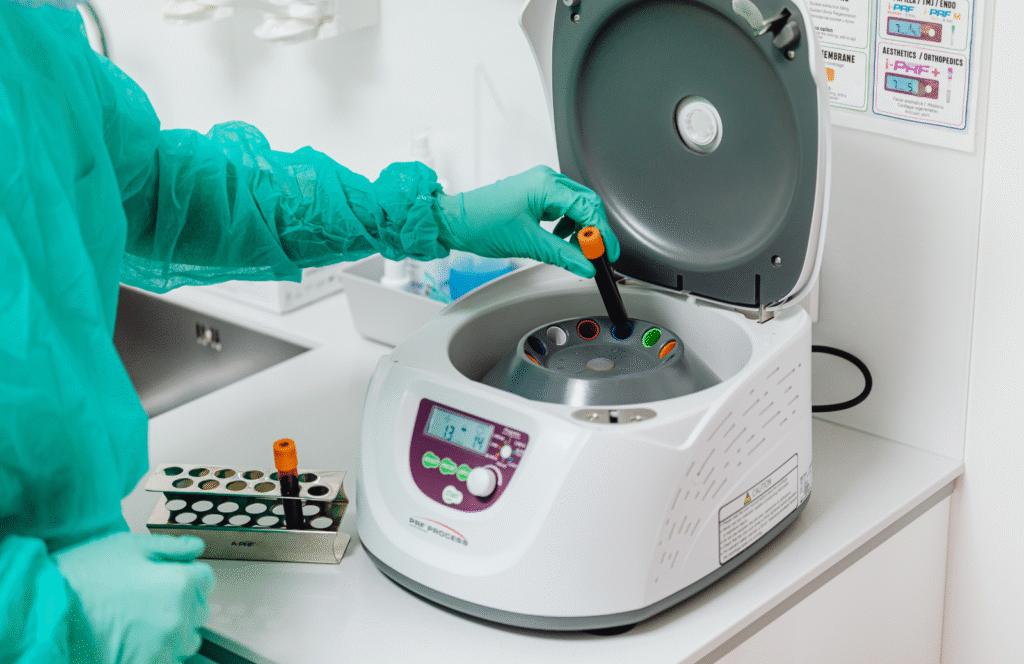
Centrifuge: A centrifuge is a laboratory device that uses centrifugal force to separate components of a liquid mixture. It works by rapidly spinning containers of liquid around a central axis, causing heavier particles to move outward and settle at the bottom, while lighter particles or liquids move towards the center. This process is known as centrifugation. Components of a Centrifuge: Rotor: The rotor is the spinning component of the centrifuge where samples are placed. It rotates at high speeds to generate centrifugal force. Centrifuge Tubes: These are containers that hold the samples. They are placed in the rotor and spin along with it. Motor: The motor powers the rotation of the rotor. Control Panel: This allows the user to set parameters such as speed and time. Safety Features: Centrifuges often have safety features like lid locks to prevent accidents during operation. Speed and Time Settings: Users must adhere to recommended speed and time settings to ensure proper separation without damaging samples. Refrigeration: Some centrifuges have a refrigeration system to maintain a low temperature during operation, crucial for preserving certain samples. Uses of Centrifuges: Separation of Components: Centrifuges are widely used in laboratories to separate components of a sample, such as blood cells from plasma or particles from a liquid. Biomedical Research: In fields like microbiology and biochemistry, centrifuges are essential for various processes, including DNA extraction and cell culture work. Industrial Applications: Centrifuges are used in industries for processes like oil separation, wastewater treatment, and food and beverage processing. Caring for a Centrifuge: Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for regular maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication. Balancing Loads: Always load the centrifuge evenly to avoid imbalance issues that can lead to damage or failure. Inspect Rotor: Regularly inspect the rotor for signs of wear and ensure it is properly seated. Lid Safety: Ensure that the lid is securely locked during operation to prevent accidents. Emergency Stop: Know the location of the emergency stop button in case immediate cessation of operation is necessary.