Gram stain:-
Very commonly used differential staining is Gram staining, used to differentiate gram-positive & gram-negative bacteria.
Developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884.
Gram’s Staining Principle:-
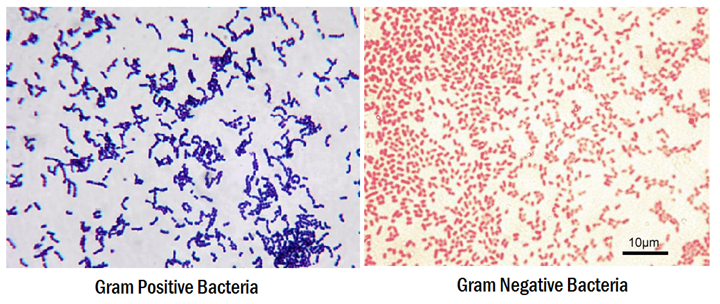
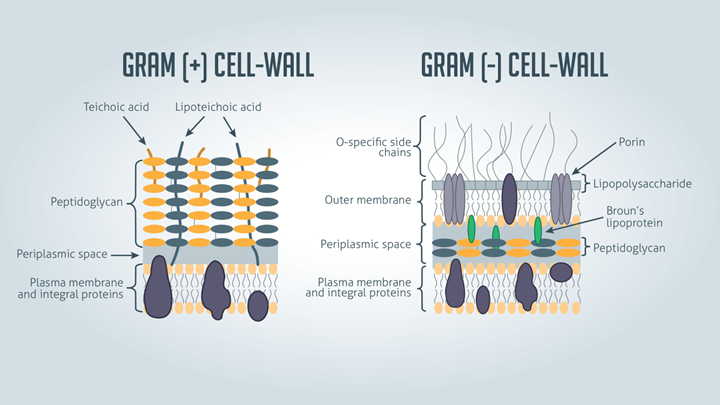
1. Bacteria having cell walls with a thick layer of peptidoglycan will resist decolorization of primary stain and appear violet or purple.
2. Bacteria having a thin peptidoglycan layer with lesser cross-linkage lose primary stain during decolorizing and gain counter stain appearing pink or
red.
3. In an aqueous solution of crystal violet dye, their molecules dissociate into CV+ and Cl– ions. These ions easily penetrate the cell wall components of both positive and negative bacteria.
4. When Gram’s Iodine is added as mordant, the iodine (I) interacts with CV+ion and forms CV-I complex within cytoplasm and cell membrane and cell wall layers.
5.When decolorizing solution (ethanol or a mixture of ethanol and acetone) is added it interacts with lipids in the cell wall.
6. The outer membrane of the Gram-Negative bacterial cell wall is dissolved exposing the peptidoglycan layer
7. The peptidoglycan layer is thin with less cross-linking in the Gram-Negative cell wall, hence becoming leaky. This causes cells to lose most of the CVI complexes.
8.Whereas in Gram-Positive bacteria, there is no outer membrane, and the peptidoglycan layer is also thick with higher cross-linkage.
9.So, the decolorizing solution dehydrates the peptidoglycan layer trapping all the CVI complexes inside the cell wall and bacteria retain the purple or
violet color of crystal violet.
10.When counterstain, positively charged safranin, is added, it interacts with the free negatively charged components in Gram-Negative cell wall and membrane and bacteria becomes pink/red.
11.Whereas, there is no space to enter inside the dehydrated Gram-Positive cell wall due to CVI complex and dehydration. Hence, safranin can’t stain them
red or pink and Gram-Positive bacteria reveal the purple or violet color.
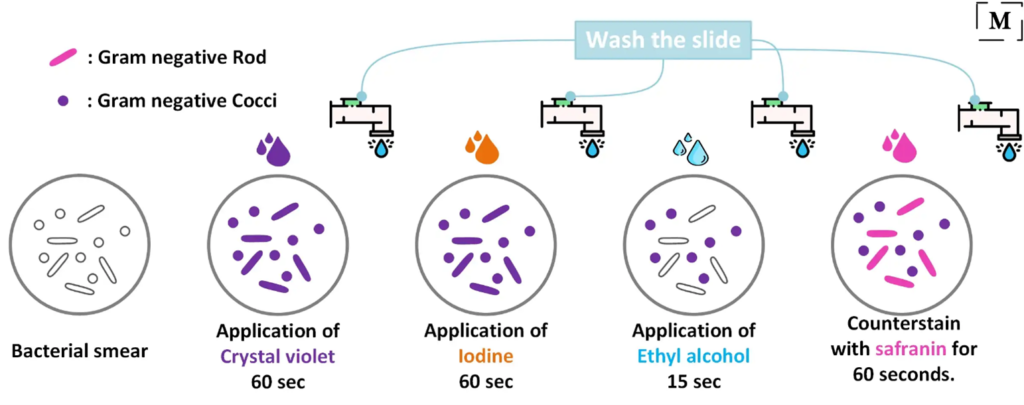
Gram’s Staining Protocol:-
• Flood crystal violet solution over fixed smear
• After 30 – 60 seconds, pour off the Crystal Violet solution and rinse with gentle running water.
• Flood the Gram’s Iodine solution over the smear
• Leave the iodine solution for 30 – 60 seconds and pour off the excess iodine and rinse with gentle running water
• Shake off the excess water over the smear
• Decolorize the smear by passing the decolorizing solution till the solution runs down in clear form. Alternatively, add a few drops of decolorizing solution and shake gently and rinse with distilled water after 5 seconds.
• Rinse with distilled water to wash decolorizer
• Shake off the excess water over the smear
• Pour counter stain over the smear
• Leave for 30 – 60 seconds and wash with gentle running water
• Air-dry or blow-dry the smear.